Living with COPD
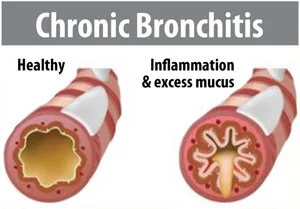 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a term used to describe a group of progressive lung diseases including emphysema, chronic bronchitis, nonreversible asthma, and some forms of bronchiectasis. COPD is a common condition that mainly affects middle-aged or older adults who are exposed to smoke. Most people don’t even realise they have the disease. The breathing problems tend to get gradually worse over time and can limit your normal activities, although proper treatment can help keep the condition under control. According to the World Health Organization report, the prevalence of COPD ranges between 4% and 20% in Indian adults. Exposure to biomass combustion fuels inside the home, lead to hazardous indoor air effluents which are associated with an increase of COPD. This is worse in the rural areas where houses are poorly ventilated. Added to this, the non-conventional forms of tobacco products such as bidi, hookah, which deliver relatively greater amounts of combustion by-products, are excessively consumed in the rural areas. This disease is mainly characterized by increasing breathlessness, generally caused by damage to the lungs over a long period due to smoking, chemical fumes, dust, air pollution, etc.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a term used to describe a group of progressive lung diseases including emphysema, chronic bronchitis, nonreversible asthma, and some forms of bronchiectasis. COPD is a common condition that mainly affects middle-aged or older adults who are exposed to smoke. Most people don’t even realise they have the disease. The breathing problems tend to get gradually worse over time and can limit your normal activities, although proper treatment can help keep the condition under control. According to the World Health Organization report, the prevalence of COPD ranges between 4% and 20% in Indian adults. Exposure to biomass combustion fuels inside the home, lead to hazardous indoor air effluents which are associated with an increase of COPD. This is worse in the rural areas where houses are poorly ventilated. Added to this, the non-conventional forms of tobacco products such as bidi, hookah, which deliver relatively greater amounts of combustion by-products, are excessively consumed in the rural areas. This disease is mainly characterized by increasing breathlessness, generally caused by damage to the lungs over a long period due to smoking, chemical fumes, dust, air pollution, etc.
Symptoms of COPD
 Some of the common symptoms of COPD are:
Some of the common symptoms of COPD are:
- Increased breathlessness
- Frequent and long lasting cough
- Wheezing
- Tightness in the chest
Who are prone to COPD
- People who smoke
- People who are exposed to lung irritants more often
- People who are exposed to a lot of second hand smoke
- People who have a family history of COPD
- People who have Asthma or history of respiratory problems
How can COPD be diagnosed?
To diagnose if you have COPD or not your doctor will:
- Do a physical examination and listen to your lungs
- Enquire about your smoking habits or your exposure to lung irritants
- Carry out breathing tests like spirometry
- Do other tests like Chest XRay and others to rule out other problems
Ways to minimize chances of flare up of symptoms
- Avoid smoking or being around second hand smoke, fume or irritants
- Use an air filter in your home
- Use mask while you are out to prevent pollutants from triggering COPD
- Keep in touch with your doctor and always have medicine at hand
- Get your flu shot, pneumococcal vaccine, and a tetanus booster that provides protection from pertussis and whooping cough
- Keep a portable oxygen unit ready for use when required
Treatments for COPD
The damage to the lungs caused by COPD is permanent, but treatment can help slow down the progression of the condition. Treatment includes:
- Quit smoking – if you have COPD and you smoke, this is the most important thing you can do
- Inhalers and medications – to help make breathing easier
- Pulmonary rehabilitation – a specialized programme of exercise and education
- Surgery or a lung transplant –this is only an option for a very small number of people
Thus, it is important to know the signs and symptoms of COPD so as to get the treatment soon. Treatment in time will help avoid future complications and distress.
Air Pollution
Air pollution has been a serious environmental problem and a major concern for public health worldwide. It continues to be a major environmental health risk, particularly in developing countries where the motor vehicle traffic and industrialization increase quickly. The respiratory system (tract and lung) is vulnerable to air pollutants, including ozone, carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, sulphur dioxide and particulate matters.
There are four main types of air pollution sources:
- mobile sources – such as cars, buses, planes, trucks and trains
- stationary sources – such as power plants, oil refineries, industrial facilities and factories
- area sources – such as agricultural areas, cities and wood burning fireplaces
- natural sources – such as wind-blown dust, wildfires and volcanoes
Air pollution is highest during the heat of the day, so plan your outdoor activities for early morning or late evening. Avoid walking or biking on busy streets. If you’re sitting in traffic, use the recycled air setting on your air conditioner to help cut down on fumes.
If you’re in a location where you can’t escape the pollution, try putting a handkerchief over your mouth and nose to help filter gas and smoke.
Antioxidant-rich foods like fruits and vegetables can also help shield your body from the damaging effects of free radicals created by air pollution.
Finally, don’t forget that indoor spaces can be polluted, too. To limit pollution at home, don’t forget to:
- Consider purchasing an indoor air purifier
- Avoid air fresheners and candles
- Keep filters on air conditioners and heaters clean
- Vacuum often
- Wash sheets and stuffed toys to get rid of dust mites
- Open the windows to circulate the air on days when the air quality is good



