Tuberculosis: Be Aware & Beware!
Poet John Keats, writer George Orwell, novelist Emily Bronte, actor Vivien Leigh, politician Simon Bolivar and poet Sukanta Bhattacharya…are all famous names who have one thing in common. We lost them all to the dreaded disease called Tuberculosis (or consumption as it was called). Today TB still remains a dreaded term even though medical science has found a cure to it. But lack of awareness and apathy has kept it almost on top of the list of diseases that cause the maximum number of deaths in the developing countries
What is Tuberculosis?
Tuberculosis is an infection, mostly striking the lungs, that kills more adults in India than any other infection. Each year, approximately 220,000 TB deaths are reported in our country and 2.2 million new cases are identifiedout of a global incidence of 9.6 million cases.6.7% of TB patients tested were found to be drug-resistant.However, TB is not an infection restricted to the lungs, it can occur in different parts of the body.
TB is curable with the correct treatment of full course of medications and stringent follow-up. Nelson Mandela, Graham Bell, Ringo Starr, Desmond Tutu andour own Amitabh Bachchanare among the famous names who have survived the dreaded disease and have led long and fruitful lives.
What Causes Tuberculosis
TB is an infecton caused by bacteria that spread from person to person through microscopic droplets released into the air by coughs, sneezes, spits, of the infected person.
Some key points about tuberculosis
- WHO estimates that around 9 million people get sick with TB per year, 3 million of these are “missed” by health systems
- TB is one among the top 3 causes of death among women aged 15 to 44
- TB symptoms (cough, fever, night sweats, weight loss, etc.) may be mild for many months, and peoplewith TB can infect up to 10-15 other people through close contact over the course of a year
- TB is an airborne pathogen, meaning that the bacteria that cause TB can spread through the air from person to person
Different kinds of TB infections:
Latent TB-the bacteria remain in the body in an inactive state. They cause no symptoms and are not contagious, but they can become active
Active TB –the bacteria causes symptoms in the infected and can be transmitted to others
Drug-resistant TB – Drug-resistant strains of tuberculosis emerge when an antibiotic fails to kill all of the bacteria it targets. The bacteria which survive become resistant to that particular drug and other antibiotics as well. Sometimes, TB patients become drug-resistant because they discontinue taking medicines once they begin feeling better. On resuming the drugs, they often test resistant
It is said about one-fourth of the world’s population is believed to have latent TB and there is a 10 percent chance of this latent TB becoming active, but this risk is much higher in people who have a compromised immune systems, like those with HIV or suffering from malnutrition, people who smoke, drug users and health care workers who treat people with a high risk of TB.
TB bacteria most commonly grow in the lungs and can cause symptoms such as:
- A cough lastingfor 3 weeks or longer
- Pain in the chest region
- Coughing up blood or sputum
Other symptoms of TB.
- Weakness or fatigue
- Weight loss
- No appetite
- Chills
- Fever
- Night Sweats
There some very common myths associated with TB which often lead to misconceptions and also incorrect treatment at times
Tuberculosis: Facts and Myths
- Myth: TB runs in the family; it is a genetic / hereditary ailment
Fact: Heredity or genes have simply no role
- Myth: There is no cure for TB or having it means death
Fact: TB is curable and effective anti-T.B. medicines are available today
- Myth: TB occurs only in the lungs
Fact: TB can occur in different organs like the Lymph nodes, Bones, Kidney, etc
- Myth: It is highly contagious and exposure to any TB patient can lead to the disease
Fact: Only Lung TB is infectious but TB in organs and childhood TB are non-infectious
- Myth: Coughing out blood with sputum means sure shot TB
Fact: Bleeding gums, sore throat, ulcers in mouth, nose bleed, pneumonia, peptic ulcer, bleeding disorders and cancer could lead to cough with blood and is not the only criteria to confirm TB
- Myth: It is a disease of the lower socio-economic class
Fact: TB can affect anyone irrespective of their socio-economic background and living conditions
- Myth: Treatment of TB is very expensive
Fact: Govt. of India provides drugs and tests for TB absolutely free of cost to Indians if they are registered with Revised National Tuberculosis Control Programme (RNTCP)
Complications
Without treatment, active tuberculosis can be fatal. Apart from the lungs, it can spread to other parts of the body through the bloodstream. Some complications of TB include:
- Spinal pain- Back ache and stiffness
- Joint damage-TB may also affect the hips and knees
- Swelling of the membranes that cover your brain (meningitis) – Tuberculosis can cause swelling in the brain membraneswhich can lead to lasting or intermittent headaches
- Liver or kidney problems –Functions of Liver and Kidney get impaired by tuberculosis
- Heart disorders –Sometimes tuberculosis can infect the tissues that surround the heart, causing inflammation and fluid collections effecting the heart’s ability to pump effectively
Testing
There are mainly two kinds of tests which are used to detect the TB bacteria in the body:
- TB skin test (TST)or the Mantoux tuberculin skin test
- Blood tests
A positive result means the person is infected with TB bacteria, butit does not classify whether he/she has latent TB infection (LTBI) or it has progressed to TB disease. Other tests, such as a Chest X-ray and a sample of sputum, are required to know whether the person has TB disease or not
Treatment
TB medications if started immediately will gradually control and finally cure the disease if the correct protocols are followed. However, the medications take a while to start acting. If you have been diagnosed with TB, then follow some simple tips to keep your friends and family from getting infected:
- Stay home – Do not go to work or school or sleep in a room with other people during the first few weeks of treatment to prevent active tuberculosis from spreading
- Proper Ventilation – TB germs spread more easily in small spaces where air doesn’t move thus good ventilation is a must to prevent it from spreading
- Cover your mouth –Cover your mouth with a tissue or a cloth anytime you laugh, sneeze or cough and throw it away when not required
- Wear a mask – Wearing a mask during the first few weeks of treatment, may help to cut down the risk of transmissionof the disease to others
- Finish your course of Medication –This is the most important step you can take to protect yourself and others from tuberculosis. Stopping or skipping treatment gives the TB bacteria chance to mutate which allow them to survive the most potent TB drugs. Drug-resistant strains are much more deadly and difficult to treat.
- Vaccination – In countries where tuberculosis is more common, infants are vaccinated with Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) vaccine because it can prevent severe tuberculosis in children.
Medicine
For Latent TB one may have to take medications for 9months/4months or 3months depending on the extent of the infection. For Active TB you will need to take a number of antibiotics for 6 to 9 months. But for the Drug Resistant TB you may need to see a specialist as soon as possible and may need to take the medications for around 20 to 30 months.

 Omega-3 Fatty Acids seem to have health benefits for people of all age groups – from before birth to old age. Infants who do not get enough omega-3 fatty acids from their mothers during pregnancy are at risk for developing vision and nerve problems.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids seem to have health benefits for people of all age groups – from before birth to old age. Infants who do not get enough omega-3 fatty acids from their mothers during pregnancy are at risk for developing vision and nerve problems.
 In kids under 12, it was found that the supplements might help in developing:
In kids under 12, it was found that the supplements might help in developing: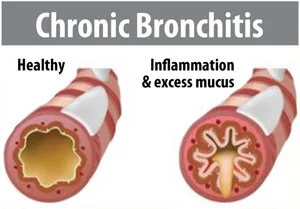 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a term used to describe a group of progressive lung diseases including emphysema, chronic bronchitis, nonreversible asthma, and some forms of bronchiectasis. COPD is a common condition that mainly affects middle-aged or older adults who are exposed to smoke. Most people don’t even realise they have the disease. The breathing problems tend to get gradually worse over time and can limit your normal activities, although proper treatment can help keep the condition under control. According to the World Health Organization report, the prevalence of COPD ranges between 4% and 20% in Indian adults. Exposure to biomass combustion fuels inside the home, lead to hazardous indoor air effluents which are associated with an increase of COPD. This is worse in the rural areas where houses are poorly ventilated. Added to this, the non-conventional forms of tobacco products such as bidi, hookah, which deliver relatively greater amounts of combustion by-products, are excessively consumed in the rural areas. This disease is mainly characterized by increasing breathlessness, generally caused by damage to the lungs over a long period due to smoking, chemical fumes, dust, air pollution, etc.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a term used to describe a group of progressive lung diseases including emphysema, chronic bronchitis, nonreversible asthma, and some forms of bronchiectasis. COPD is a common condition that mainly affects middle-aged or older adults who are exposed to smoke. Most people don’t even realise they have the disease. The breathing problems tend to get gradually worse over time and can limit your normal activities, although proper treatment can help keep the condition under control. According to the World Health Organization report, the prevalence of COPD ranges between 4% and 20% in Indian adults. Exposure to biomass combustion fuels inside the home, lead to hazardous indoor air effluents which are associated with an increase of COPD. This is worse in the rural areas where houses are poorly ventilated. Added to this, the non-conventional forms of tobacco products such as bidi, hookah, which deliver relatively greater amounts of combustion by-products, are excessively consumed in the rural areas. This disease is mainly characterized by increasing breathlessness, generally caused by damage to the lungs over a long period due to smoking, chemical fumes, dust, air pollution, etc. Some of the common symptoms of COPD are:
Some of the common symptoms of COPD are:
